The importance of malt in brewing
Malt provides:
- enzymes and starch for the production of alcohol and carbon dioxide;
- organoleptic compounds that determine the beer's flavor profile;
- color, based on the intensity of the chemical reaction during kilning;
- and proteins, which boost yeast activity and provide body.
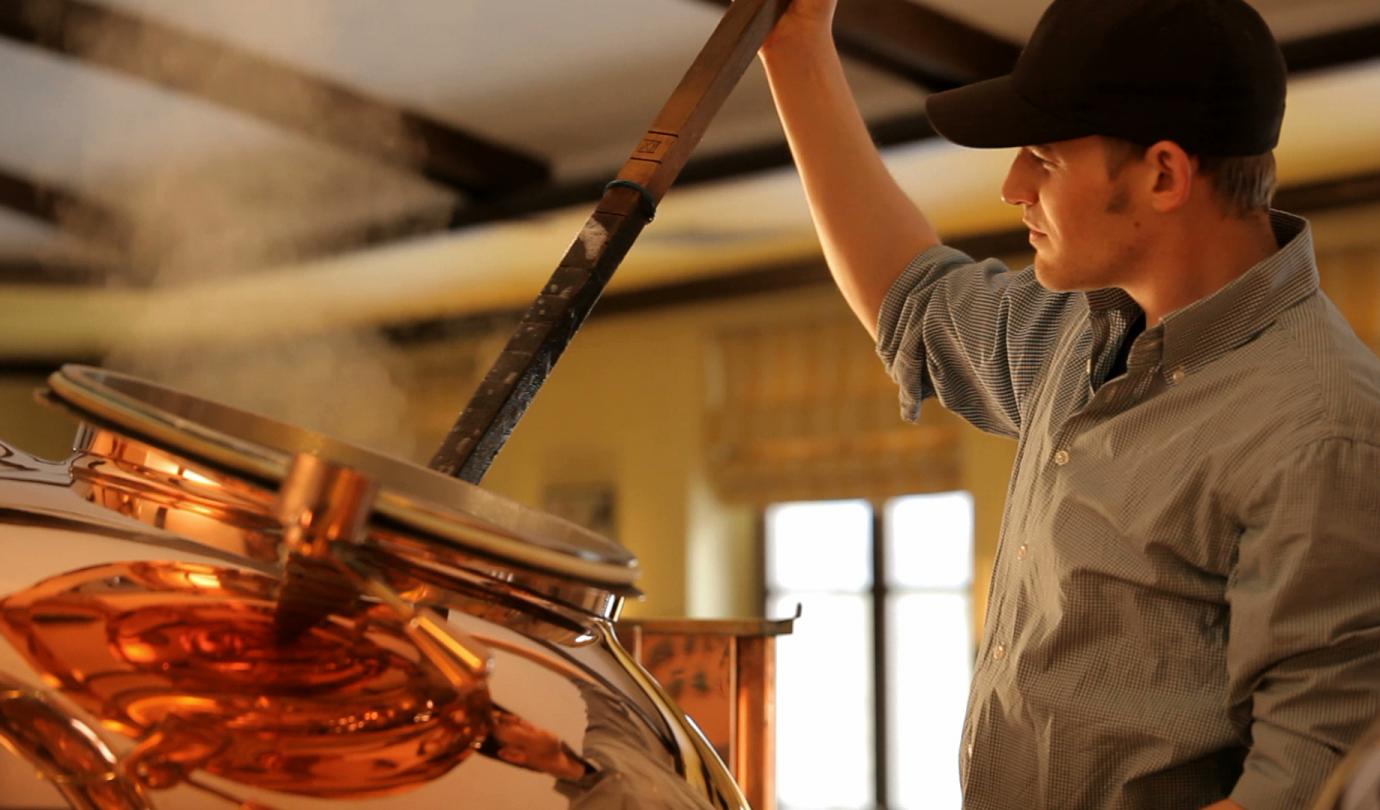

The different types of malt
There are many types of malt: Pale, Pilsen, Vienna, Munich, Caramel, Peated, Diastatic, Roasted and Chocolate, among others.
Their characteristics depend on the malting process used. Roasted malt, for example, is obtained using a method that is similar to the process used for roasting coffee. Dark malts are used for brown ales or stouts, whereas pale malts are used in lagers and "Pilsners".
We also produce wheat malt, used mainly for white beers.

What is malt quality?
A good malt must first and foremost meet its customers' needs.
At Malteurop, we design products to meet breweries' and distilleries' exact specifications. We adjust parameters such as moisture, grading, or extract, to get the malt quality desired. We can also adapt viscosity, beta-glucan content, friability, and alpha-amino nitrogen content.
Good malt quality is testament to both a good process and good control of sanitary conditions.

The stages of brewing
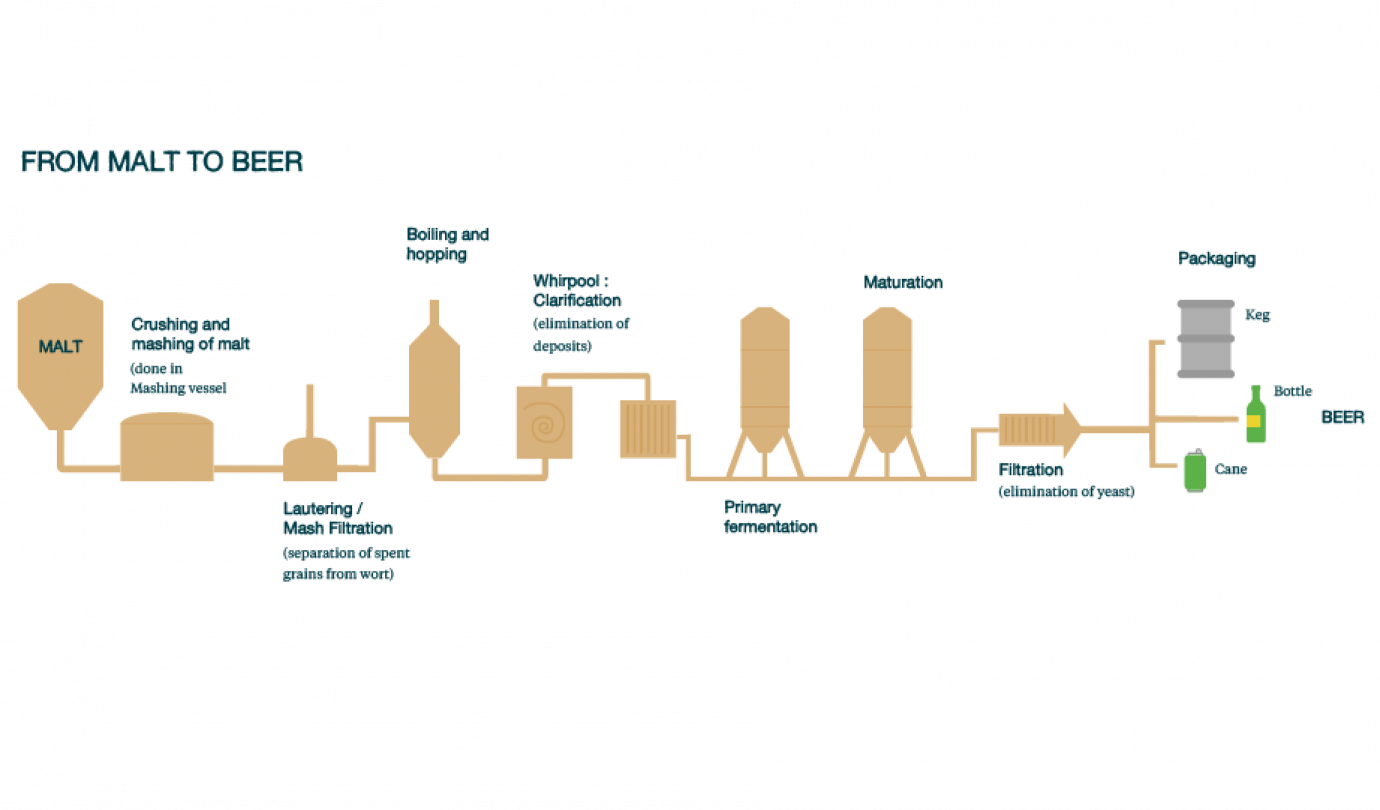
From barley to beer
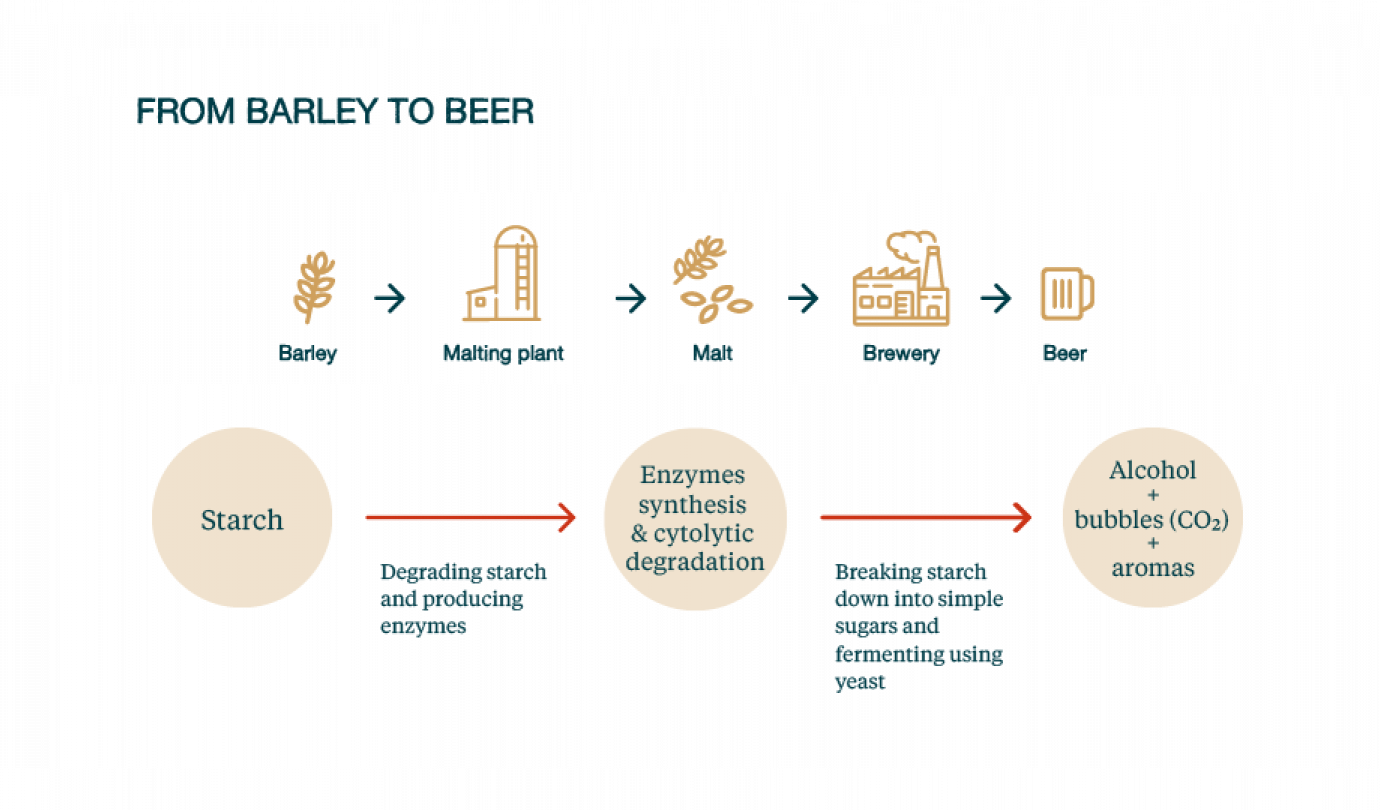
Find out more about the whiskey production process
The term "whisky" designates any alcohol obtained by distilling fermented grain, whether it be malted or not.
To obtain the "malt whisky" designation, you need to meet strict criteria. Malt is used at several stages of the production process.